Enhance your curriculum by addressing the QAA Guidance on skills for your subject, and incorporating the QAA (2018) Guidance on Enterprise and Entrepreneurship.
The following ETC tools can help you to deliver these skills in the curriculum
These guides have been selected to build QAA (2018) enterprise skills in your teaching.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6), Individual Task
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
7Communication and Strategy
This task focuses upon visual representation of problems and how this helps define a situation. It is essentially the transmission of ideas into pictures. It is used to stimulate participants in a programme to express themselves and their ideas in a pictorial form, often with the use of metaphor. It then stands as a basis for discussion of participant ideas and concepts.
This approach is recognised within some subject specialism as a rich picture, as a way to explore, acknowledge and define a situation and express it through diagrams to create a preliminary mental model or visual representation of the situation or challenge. A rich picture helps to open discussion and come to a broad, shared understanding of a situation.
Participants are asked, usually in groups, to discuss the meaning of a concept or an event or to explore a situation or problem. They are asked to portray this in pictorial form as a basis for presentation and discussion with other participants.
The approach can be used in a number of ways but most importantly to test understanding after readings and discussion and, to harvest pre-conceived views and attitudes relating to a subject as a basis for discussion.
If you wish to focus the activity, you can ask the group to identify opposing elements inherent within their challenge and use these are axis. So a groupmight identify “speed” as a key element of an activity (such as inherent within the eating-out experience) and also “service”. This would create two axis of Fast and Slow (for Speed) and High levels of service with No service. This creates four quadrants that they can seek to describe through a rich picture. This would show what fast, high level of service restaurant experience would be like, against a slow high service experience etc. You can then invite them to title these quadrants and explore them for benefits/costs.
The exercise aims to stimulate creative expression. It also is designed to give ownership of learning to participants by creating discussion on the basis of their existing knowledge and ideas. With sufficient pens available, there will be no ‘lead author’ and therefore a strong basis for mutual understanding is created. A sense of ownership is given to the group and participation in learning is maximised.
Explore with the whole group the power of visual presentation and their perceptions of their involvement. Explore their satisfaction with the finished product and how well they feel it worked as a mechanism for communicating with a group.
Gibb, A and Price, A “A Compendium of Pedagogies for Teaching Entrepreneurship” ncee 2nd Edition, 2014; first published in 2007
http://ncee.org.uk/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/Compendium-of-Pedagogies.pdf
Seek additional guidance relating to Rich Pictures from work within Soft systems methodology
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Lecture Theatre
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
7Communication and Strategy
Engaging large groups of students in delivery and content interactively can be a challenge, often made more difficult by the lay-out of teaching spaces. Using the potential of the mobile or smart phone for texting, voting, or twitter can engage all the individuals in the room, allowing them to ask questions that are unlikely to be raised as questions during a traditional lecture format.
Engaging students in their learning, particularly in the static environment of large lecture theatres is a challenge. However learners are likely to have smart phones available to them during class and rather than banning them from the room, it can be more engaging to encourage your students to use their phones to raise questions, vote and share their opinions or indicate their views on specific topics. By developing your traditional‘lecture’ style to involve decision points, questions or votes, you can check understanding in the room, and if you wish to use specialised text apps or features (such as Twitter or voting apps) you can open your entire input to comment and reaction.
This activity can be incorporated into your traditional large group teaching (particularly with large group or in lecture theatre) and although it doesn’t specifically take much time to set up and engage them, you need to ensure that you allocate time for discussion of any points within class to review and clarify the learning. By creating point of engagement, or inviting students to comment you can change the dynamic of your lectures and develop a ‘conversation’ not only with the learners and yourself, but also across the learners together.
Note of caution: obviously this approach needs consideration relating to the age range and appropriateness of this type of engagement. There are issues of privacy when using texts (phone numbers) and providing open communication, such as a full twitter ‘wall’ can lead to humour and irrelevant topics appearing on the screen which become distracting to your educational message. You however have the choice to open this screen fully to your students throughout the class, making all communications visible (if using twitter etc) either on a screen or through individual phones or lap tops, or you can keep this dialogue direct to you. Ownership of accounts (such as in twitter) create a more direct link to individuals without disclosing personal contact details, but it is important to agree ground rules of respect to avoid any trolling of those actively engaging. Typically students are responsible when engaging with this public forum, but it is important that you are clear about the need to respect contributions and those making them.
In allowing the learners to voice their concerns, vote on their views and share their feelings or confusion you are opening up their learning experience and showing that other students, as well as themselves as individuals, can develop and deepen their understanding through discussion and clarification. The skill of concise and effective communication is displayed in the voting and within the precision of short texts or 140 characters in twitter. This task builds confidence if you, as the tutor, welcome comment and develop the “conversation” with your learners. It is important to acknowledge questions and areas of concern and respond within the class, or specifically state when you will review this topic further, to create a legitimate feedback loop between yourself and students.
Note: Check that students have access to mobile or smart phones and that they are happy to engage in learning by sending text messages (many phone packages allow for free texts but it is important to understand the group perception/position on undertaking this task before starting as it may involve expense). If wifi is available, then many of the features of apps will be free to use and typically university students have access to institutional wifi in order to engage. However you need to check that your particular teaching room will support your proposed activity without students incurring costs to engage.
A little preparation can be needed (either for individuals to prepare (or establish an account) and/or the tutor to establish twitter accounts or to familiarise yourself as the tutor with specific apps, such as Poll Everywhere http://www.polleverywhere.com/ or a twitter wall to display (such as https://tweetwall.com/ or similar). There are lots of different applications available which will display tweets, or visually display votes or words from students, many free to use, so consider the constraints of your teaching room (such as wifi enabled etc) and encourage your learners to be prepared in advance by making any downloads required.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
This approach to creative thinking structures thinking through the use of a mnemonic "SCAMPER" and using questioning techniques to generate solutions. This makes an ideal group activity for students to work through the mnemonic and then present their results.
Students are placed in small working groups and invited to explore the seven prompts of the SCAMPER mnemonic. Firstly, invite each group to take an existing product or service (or agree one to consider - this could be one that you want to improve, one that you'recurrently having problems with, or one that you think could form future product developments).
Questioning around these themes helps the groups develop creative ideas for developing new products, or services and for improving current ones. SCAMPER is a mnemonic that stands for:
Using these headings, invite each group to discuss the questions about the product, using the mnemonic.
By brainstorming as many questions and answers within each group, a rich solution can be produced.
Example Questions which you can share with groups in need of support.
Substitute: Ask "What can you substitute? What can be used instead? Who else instead? What other ingredients? Other material? Other process? Other power? Other place? Other approach? Other sounds? Other forces?"
Combine: What can you combine or bring together somehow? How about a blend, an alloy, an assortment, an ensemble? Combine units? Combine purposes? Combine appeals? Combine ideas?
Adapt: What can you adapt for use as a solution? What else is like this? What other idea does this suggest? Does past offer a parallel? What could I copy? Who could I emulate?
Modify: Can you change the item in some way? Change meaning, colour, motion, sound, smell, form, shape? Other changes? Or Magnify: What can you add? More time? Greater frequency? Stronger? Higher? Longer? Thicker? Extra value? Plus ingredient? Duplicate? Multiply? Exaggerate?
Or 'Minify': What can you remove? Smaller? Condensed? Miniature? Lower? Shorter? Lighter? Omit? Streamline? Split up? Understate?
Put to Another Use: Can you use this product somewhere else, perhaps in another industry?
Eliminate: What can you eliminate? Remove something? Eliminate waste? Reduce time? Reduce effort? Cut costs?
Reverse: What can be rearranged in some way? Interchange components? Other pattern? Other layout? Other sequence? Transpose cause and effect? Change pace? Change schedule?
Evaluation:
Once the ideas have been generated, the next stage is evaluation. Through group discussion, ask the student to determine ifany stand out as viable solutions? Could any of them be used to create a new product, or develop an existing one?
All viable ideas can be explored further in order to find one improvement/suggestion for final presentation to the wider group.
A debrief on the solutions, the process and the team working should be included within the session to allow for the skills and emotional aspects of team work to be explored, and the constructs of the mnemonic discussed.
Although the main focus of this project is idea generation, the discussion and evaluation within the group, which requires presentation and interpersonal skills as well as judgement and critical analysis of opportunities and ideas.
Student groups should be left to work through their discussion, and any difficulties with team working as may occur (intervening only to support the process and move the students on, if time pressures require) however it is important to review the task, the process and the protocols in order to seek guidance for future working or lessons to take forward.
Students should be encouraged to share the frustrations and difficulties of decision making within a group (where one individual may have suggested the idea) and how feedback should be given and shared.
Group dynamics need to be acknowledged and lessons can be shaped for future team working.
http://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newCT_02.htm
http://www.brainstorming.co.uk/tutorials/scampertutorial.html
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Presentation Space
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
7Communication and Strategy
This physical task engages the whole person in supporting a colleague and ensuring their safety through good communication. The activity can be used at any time during the session, however it is highly effective as and ice breaker. It is a fun method to start participants communicating and is simple to deliver in an appropriate environment and can be adjusted depending upon group size, age etc. However health and safety is paramount and you must consider the appropriateness of the group and room for this challenge.
You should initiative this activity by stressing the nature of the challenge and stressing that the safety of those involved is paramount. You can also agree across the group that “stop” can be initiated by any member of the team by raising a hand if they don’t feel that it is safe to proceed. This can be actioned by anyone and will not result in any penalties.
To run the task, gather the group outside the room and:
It could also be possible to create a preferred route or course (as seen in horse show jumping) which they need to accomplish (if you didn’t wish to use obstacles for safety or mobility reasons) which would lead the pair to particular numbers/letters indicated on the wall.
Subject specialisms could also be tested by placing knowledge based answers on the walls and asking the pairs to walk to their answer through the course (see QAARunaround for details of how to do a multiple choice but don’t mix the games in play for safety reasons).
This task requires listening and communication skills and also helps builds trust and connections across the pairings. However the skill development and improved future practice comes from evaluating performance across the group and understanding how and when particular techniques were effective and what lessons that provides for the future. It is important to acknowledge fears and concerns, or frustrations between the pairings but keep the discussion to the general learning, rather than focusing upon particular experiences of individual pairings as the depth of learning will come from the lessons that can be applied in future group work or communication challenges. These lessons include clear communication; agreeing ground rules for working together; recognising the need of feedback or support; understanding the importance of clear short messages within these circumstances etc.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
This task focuses a group of people to organise themselves to set up a production line to exactly replicate an existing product as many times as possible in set amount of time. They are giveqaan the opportunity to reflect on and improve their approach twice to increase efficiency, quality and productivity. This gives participants and others the opportunity to see how their own and other behaviour, ideas, approach affects the development and outcome of the task and how by working together and reflecting and analysing a situation it can be adapted and improved going forward.
This activity could take from 30 minutes to a couple of hours depending on how much review, reflection and analysis takes place at the end of the session.
Group gathers around a table with all the resources on it. There is a sample product : a booklet with 13 squares of paper 10cm x 10cm, secured with 2 staples in a x shape in the top left hand corner of the booklet.
The group is asked to put together a production line replicating this booklet. They will have 2 minutes to discuss how they think they could best do thisand to allocate roles. Then 3 minutes to put this into practice and produce as many booklets as possible. When the time is up the facilitator then countsand inspects the finished products, looking for quality and accuracy ie:
The group then gets 2 minutes to discuss and review their methods, systems and procedures and come up with improvements or a different approach. They then get another 3 minutes on the production line to best their last score.
The above process is then repeated for a third time.
This could be done with any size group as long as there are sufficient facilitators to split into smaller groups. The optimum numbers in each group wouldbe between 6 and 10, however multiple groups could be working at the same time. They would have to work at the same time so as not to hear the discussion of other groups.
Skill Development:
As has been described this task involves many different skills and objectives on all different levels and can be assessed and analysed either briefly or in great depth across some or all of the objectives. For example, if this is an exercise for managers or recruiters to assess staff skills and abilities it can be finished there at the end of the last count. However it can be extended further, so each team then breaks off with a facilitator to analyse what happened at each stage and why.
For example : the focus could just be on the outcomes, ie the quality and quantity of the finished products. Often the first time, people are rushing and slapdash and may do quite a few but get a lot rejected, so need to slow down. Or get them all passed but do a small number, so need to speed up. So it's finding that balance between speed and quality/accuracy.
Or the focus can be on the review and reflection, how the method was changed or improved each time to give better results.
Or the focus can be on the team dynamics how they evolved through each stage, or on the leadership and management of the task and how that changed and fluctuated at each stage, how the balance of power shifted as the task went along.
Or it could very much focus on the individual, the role they played, how this evolved, how they felt, how they were affected by the different characters,how they affected other members in the group, positively or negatively what they would do differently next time.
Depending on whether the focus is on 1 or 2 of the objectives and skills or all of them, all of these and more angles can be identified and explored after the task.
Large sheets of paper (A3 or larger, could use old newspapers) minimum of 60 sheets per team, pens, pencils, markers, rulers, scissors, staplers.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Outside
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
This exercise is a fantastic way to get people working together as they tackle up to 10 tasks in a given time frame. With limited information (on each other and the tasks presented) the group must navigate through the challenges in order to be the most successful group (back within the time frame; most tasks achieved; most accurate delivery of the tasks). Depending on the tasks selected, specific industry or sector knowledge can be tested as widerskills of background knowledge, research and creative thinking are required. Insist upon evidence of the achievements (photos on flip or camera phones) as well as delivery of objectives.
Activity : This activity needs a long session (such as 120 minutes) to complete, reflection and analysis takes place at the end of the session.
The groups of up to 6 people are sent out to complete > 10 tasks (usually 3 cryptic, 3 researched and 4 fun)
Examples of these could include:
These tasks should be developed beforehand to suit the environment where the day is taking place. Ensure there are fun tasks involved and that everyone has a chance to engage by creating a range of challenges that involve the physical, mental, social aspects of your learners.
To manage this challenge effectively, if it important that you:
Practically it can also be helpful to give them a puzzle to solve before they can leave and a further one when they return. This means they are leaving at different times and they return to a final challenge, so that you can record time and award points.
Depending upon the challenges you create, there is a wide range of transferable skills and knowledge base that you can test during this challenge. You can create tasks that draw upon their:
It is important that you review the challenges and how the groups tackled the tasks in order to draw out the subject learning and these wider skills, before reviewing the wider team experience by exploring:
Drawing out the team dynamics will allow the students to identify the lessons that they can take forward that will improve their future group work and learning experiences.
Ask if they started by sharing their knowledge and skill set or just started on the tasks (the most typical response) and whether they would do that again. Ask when, or if they ever start a task by reviewing when they have collectively or individually undertaken something similar and what was learnt that they could take forward.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
Effective engagement of Alumni seeks to support the students to become:
With the pre-arranged (and prolonged) support of alumni (now professionals) this approach of continued access to external professionals (ideally programme/course Alumni) is designed to prepare students to be able to engage with real clients and better enable them to respond proactively to change.
Externals are invited to engage with the current student group as they undertake a task, using social media (facebook; twitter etc) an/or Skype. This creates either incremental weekly instruction that builds into an overall assignment or regular support or feedback on course work from externals.
This approach needs pre-agreement and commitment of externals (ideally Programme/course Alumni) who commit to short, but regular interaction through social media or Skype.
This activity can either be driven by a live brief or challenge identified by the external (higher level of engagement) or as comment and support to those undertaking the programme, through sharing expertise and current work experiences. If the students are working on a live brief or task given by the external, this high level of interactivity can mean that summative deadlines can changedand information updated, and the newsworthy or other high profile influences can be included throughout the module. (The assignment usually mirrors an actual assignment undertaken professionally by an Alumni professional).
This engagement can be “managed” by the tutor – to pre-plan some ambiguity or pre-agreed change of brief/scope with the Alumni contact, or left open to allow access to externals as an organic relationship, where advice may be sought by the students or experience/daily practice shared by the Professional as they see fit.
In addition, any presentation /show case or final assignment submission can be shared with the external and their input made part of the summative or formative feedback (assessment strategy).
Note that the choice of social media will impact on the type of engagement between alumni and students, but ideally something that the Alumni member uses regularly will ensure more regular engagement. Even small inputs (as typically seen in social media such as Twitter) can guide student approach and ensure that they are able to ask private questions, and that other students can also learn from the mentor/alumni generic comments or insights.
Depending upon the level and type of engagement, students can benefit from insights from a ‘typical day/week’ of a professional working in their area, or be pushed to develop their tolerance to ambiguity (through changing deadlines, or unexpected changes to the brief or additional information). This can build resilience in the students but there needs to be clear expectations of this relationship, as well as additional tutor support.
Students typically respond well to changes and additional insights from professional Alumni and can develop their understanding and judgement, in their chosen field, whilst gaining further insight regarding professional practice.
Students should be bought together to share their experience of virtually engaging with their Alumni contact and explore their emotional responses to the changing briefs or additional information. They need to explore, and develop strategies, for coping with ‘real world’ brief/challenges and exploringthis together, and sharing how they dealt with it, and could deal with it in the future, builds their confidence and resilience to change. Using reflective practice to consider the learning across the group can draw out a range of key lessons for preparing for future challenges.
Access to, and ongoing (committed) virtual engagement by appropriate alumni – determine brief/project or to commit to regular updating/comment for a pre-agreed period of time.
Penaluna, A., Penaluna, K and Diego, I. (2014) The role of education in enterprising creativity. In Sternberg R and Krauss, G. (2014) Handbook of Research on Entrepreneurship and Creativity. Cheltenham / Massachusetts: Edward Elgar).
Scott, J., Penaluna, A., Thompson, J & Brooksbank, D. Experiential entrepreneurship education: Effectiveness and learning outcomes. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour and Research (Forthcoming)
Jones, C., Penaluna, A., Matlay, H., Penaluna, K. Discovering the Soul of Enterprise Education. Education +Training, Emerald Publishing (Forthcoming)
Penaluna, K., Penaluna, A., Jones, C. and Matlay, H. (2014) ‘When did you last predict a good idea?: Exploring the case of assessing creativity through learning outcomes’, Industry and Higher Education, Vol.8, No.6, December 2014: 399 - 410
Penaluna, A., Coates J. and Penaluna K., (2011) Creativity-Based Assessment and Neural Understandings: A Discussion and Case Study Analysis. Education + Training, Emerald Publishing, Volume 52, Issue 8/9, pp. 660 - 678
If you would like to have your How to Guide featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the How to Guide.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Lecture Theatre, Presentation Space, Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
Objective:
The ‘Commercialising Innovation’ module seeks to address a frequently identified need for engineering graduates who recognise and can engage in agendas of innovation within industry settings.
Key points
Introduction:
Following a period of initial curriculum development support from Cardiff University Enterprise Dr Jeremy Hall now leads a Cardiff School of Engineering module that develops an awareness of innovation and commercialisation.
The ‘Commercialising Innovation’ module is now offered to all 3rd year (NQF level 6) mechanical and electrical engineering students. Initially delivered as an option to just 15 students in 2011-12, numbers have grown to 50 (capped) for 2013-14. The module has been replicated within the School of Physics and Astronomy enabling some cross disciplinary delivery and collaboration.
The QAA subject benchmark statement for engineering (2010) consistently advocates the embedding of innovation and creativity learning and aspects of commercial management training within engineering curriculum design in order to promote the development of economically viable sustainable solutions from within industry.
The Royal Academy of Engineering 2012 document ‘Educating engineers to drive the innovation economy’ strongly advocates an embedded approach to the teaching of radical innovation and commercialisation processes via immersive experiential learning and simulation techniques. Published since the first roll out of the Commercialising Innovation module, this document evidences contemporary attitudes and approaches to engineering based enterprise education and substantiates the cutting edge pedagogical methodologies and learning aims adopted by the module.
The ‘Commercialising Innovation’ module seeks to address a frequently identified need for engineering graduates who recognise and can engage in agendas of innovation within industry settings. Using Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education guidance for the development of enterprise and entrepreneurship education (2012) the module cultivates understanding of the processes of commercialisation whilst developing core enterprise skills and behaviours among students. The recent partnership between Cardiff Schools of Engineering and Physics in the delivery of the module reflects the needs of industry for graduates who have the appropriate skills in order to work collaboratively with colleagues from a variety of differing disciplinary specialisms in order to take innovative ideas to market. Exposure to one another’s discipline in the context of the commercialisation module provides students with insight into the potential modes of application of their own disciplinary learning.
Activity:
The core learning activity undertaken by students is centred upon an experiential learning scenario.
Considering team dynamics, learners engage in ‘company teams’ in the simulated commercialisation of a discipline specific innovation and its associated commercial development. Learning tasks are approached by students in the context of ‘company teams’, Teamwork provides fertile ground for the development of practical enterprise and employability skills, with emphasis placed on fostering personal responsibility towards the team activities.
Theoretical and practical learning is contextualised by the use of real world examples of discipline/sector specific innovation commercialisation, communicated to learners by experienced and relevant external speakers and the use of pertinent case studies and activities. Students engage with a comprehensive range of enterprise skills and associated learning outcomes. Summative assessment for the module required learners (as part of ‘company teams’) to generate a feasibility study and deliver a time constrained presentational pitch for their company to a panel comprising some of the guest speakers. Additionally each individual is required to submit an individual reflective report requiring them consider development against learning objectives.

Impact:
In the first year of module roll out it reached the top 10% for positive feedback against all engineering modules offered at Cardiff University. This may go some way to explain the rapid advancement in take up to a point where now the module has now had to be capped at fifty (due to the highly interactive nature of the learning processes). Learner feedback demonstrated an appreciation for the teaching and assessment approaches employed and revealed a genuine sense of functional skills development. Many learner reflections have revealed a strong awareness of the practical value of the skills and experience gained from participation in the module and it has been viewed as a valuable complement to the predominant engineering elements of their degree programme. In addition facilitators involved in the design and delivery of the enterprise learning module have found the experience valuable, rewarding and inspiring with regards to future module development.
Academic feedback;
“The challenge has been to develop an authentic taste of the wide-ranging process of commercialising real value from engineering. Not all students will want to become entrepreneurs but many of the skills this training provides will be relevant to the workplace for engineering graduates. I hope that my experiences in setting up a university spin-out has fed through to a realistic, and strongly interactive learning experience which has assisted the successful entry of our students into their working lives.” Dr Jeremy Hall, Senior Lecturer, Cardiff School of Engineering (2014).
Learner outcome:
Student feedback;
“The description of the module was to develop commercial awareness of engineering innovation and the module did exactly this, I now possess a better understanding of the process of commercialising an idea and have developed an understanding of Intellectual Property, marketing techniques as well as general business practices. I also have a more thorough understanding of the type of companies that operate within the UK and can appreciate how the size of the business can affect the structure of it. Whilst obtaining commercial skills during the module, it has also improved some of the softer skills that are needed in industry such as self-confidence and communication skills.” Engineering student B (2012)
“The skills gained in the class this semester were so many not just in terms of starting a new company or building a business plan but also helped us in improving our communication skills, negotiation skills, presenting and most importantly the team work skills. So it can be said that the module has created a confident engineer and enabled him to innovate and sell his product.” Engineering student C (2013)
The examples of curriculum development for enterprise related outcomes were originally outlined by Neil Coles at the International Enterprise Educators Conference under the heading 'From Archaeology to Zoology; an A-Z of enterprise in the curriculum'. For his work in contextualising enterprise for any subject, Neil won the 2013 National Enterprise Educator Award.
Resources:
References:
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
Objective:
‘Renewable Energy Enterprise and Management (REEM) is a unique multi-disciplinary course blending appropriate project evaluation techniques and business enterprise with awareness of the potential of renewable energy technologies. The distinctive flexible learning approach blends distance learning with intensive face-to-face weeks on campus.’
(http://www.ncl.ac.uk/postgraduate/courses/degrees/reem-msc-pgdip-pgcert/#profile)
Introduction:
Katie Wray, Lecturer in Enterprise, Newcastle University;
“In Renewable Energy there are 2 MSc options at Newcastle University, MSc Renewable Energy, Enterprise and Management (REEM) and Renewable Energy Flexible Programme (REFLEX). REFLEX is for applicants that have a hard engineering first degree: REEM is open to students from a wide range of technical and non-technical backgrounds.
Activity:
“REEM is structured as a year-long programme made up of block teaching weeks (10 credits = 1 full week of teaching plus a pre- and/or post- school assessment). The programme introduces enterprise and entrepreneurship as shown in red below.
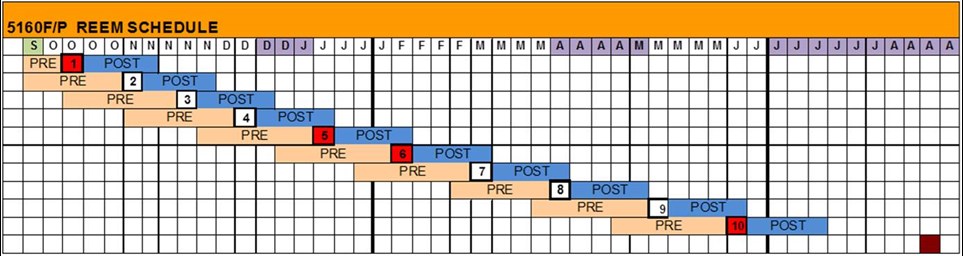
Figure 1
“This gives the foundations at the beginning and end of each semester to ensure that the theme of enterprise and the application of the technical, project and policy modules is reinforced throughout.
“Students undertake practical enterprise training during these modules as well as undertaking an Enterprise Project dissertation, in which they undertake a business plan or feasibility study into a new opportunity for renewable energy.
“By teaching in a block week format, it is possible to simulate a boot-camp style learning experience during an intensive week, and to build good peer relationships which would otherwise not be possible outside the classroom. Some examples of the topics covered in the 2 modules are shown below.
Figure 2: SPG8015: Introduction to Enterprise and Entrepreneurship in Science and Engineering

Figure 3: SPG8016: Business Enterprise in Science and Engineering
Impact:
“The students have independently created an interest group for both REEM and REFLEX (started by someone on REFLEX) for students that are interested in enterprise and entrepreneurship. The group is like an informal society. It is based on opportunities emerging in Renewable Energy or Energy Management.
We see students applying for these programmes do so because they have identified some growth opportunities in the sector.”
Learner outcome:
These examples of curriculum development for enterprise related outcomes were originally outlined by Neil Coles at the International Enterprise Educators Conference under the heading 'From Archaeology to Zoology; an A-Z of enterprise in the curriculum'. For his work in contextualising enterprise for any subject, Neil won the 2013 National Enterprise Educator Award.
References:
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6), Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
6Interpersonal Skills
To develop an interdisciplinary network of exchange which promotes innovation, design thinking, new-product development. Bringing together a students from across the University, who value innovative thinking, ideas generation and interdisciplinary working as part of their student experience.
Interdisciplinary has been recognised as a key contributor in solving complex global social problems (BIS, 2009; 2009a; DIUS, 2008, QAA 2012). It therefore follows that graduates as societies leaders with a genuine interest in making the world a better place must have the ability and confidence to work across disciplines. In today’s global economy and in society as a whole, we are faced with many complex challenges which require new ways of working and graduates need to be prepared for this through the integration of interdisciplinary working within their under graduate (UG) curriculum.
The 24 hour design challenge: Second year students from across 3 schools within the university were invited to register for this event, places were limited to 40 students, a maximum on 10 students from a single discipline area.

The impact on learning was evident through the student feedback, we categories it into skill development, Collaborative working, Entrepreneurial development.
“There is never a stop-point in learning – there is always room for more”. (2015 student)
“Competing in this design challenge was a thoroughly enjoyable process. As an engineer, it is important that I develop the ability to work with multiple disciplines and in the 24 hours we were given I have been given a massive insight into how completely separate skill sets can come together to generate an idea. I also find it incredible that after only a day, I came away with a team that I had formed a friendship with and now have an insight into demonstrating an idea to someone who has the means to make it a reality. Overall I cannot fault the opportunity of taking part and enjoyed every stress inducing minute of it. I would definitely do something similar again.” (2014 24 hour design challenge).
Skill-development:
“....in the 24 hours we were given I have been given a massive insight into how completely separate skill sets can come together to generate an idea” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“It was an enjoyable challenge, bringing in different skills we have learnt throughout our time here so far. I would defiantly recommend it to anyone and do it again” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“…enjoyed every stress-inducing minute of it. I would definitely do something similar again” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“I learned a lot from my peers in my team and this experiment will benefit me in future group projects” (student quote, 2014 challenge).
Collaborative working:
“....I really enjoined the challenge and it was good to start viewing things from different discipline angles” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“This design challenge was great. I love working with all of my team who were from different specialisms” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“It has shown me what some of my lecture have been trying to tell us which is that collaboration and working with people from different specialisms is when design can really take off and become exciting” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“I really enjoyed the 24 hour challenge as I valued meeting new people and exploring different areas of study” (student quote, 2014 challenge).
“It was really helpful to speak to the different tutors and pick their brains about our ideas, as I would never normally come into contact with tutors from these courses” (student quote, 2014 challenge).
Entrepreneurial development:
“The challenge has made me even more interested in working with people I don’t know and also has inspired me to think about business ideas for my future career” (student quote, 2013 challenge).
“It was a great experience, thank-you! It is a great insight to the business world that we are entering” (student quote, 2013 challenge)
“Overall it was a great experience and I now have contacts and friends on completely different courses to me who I will no doubt be calling on for help on future projects as well as the one we started” (student quote, 2014 challenge).

Comment from external Judge: “Judging the 24-hour design challenge was a pleasure and revealed an impressive arsenal of talent the University of Huddersfield has amongst the students. Each multi-disciplined team presented well thought out and researched concepts which impressed the judging panel and stimulated much debate. Being spoilt for choice meant the pressure was put back on the panel when it came to us choosing a winner. In my experience, great ideas occur when a creative person or team is constrained by time and/or budget. When placed under pressure, right brain instinct coupled with pragmatic decision making, causes inventive and exciting concepts and solutions. Events like the 24hr Design Challenge are a great example of where you'll see this in action.” (David Bailey Creative Director UX&D, BBC Future Media).

The learning is not within the task objective, but within the team process, networking and cross-fertilization of skills and often the desire to complete the task can mask the transferable learning that has been gained. It is therefore key, that once the discussion of the challenge itself is complete, that the de-brief encourage the teams to explore the skill development within the task and team work itself. As a facilitator, it is important that you allow the teams to explore their team process and find the learning within that. Within the dragon’s den the teams are asked to reflect on this experience.

BIS (2009). Skills for growth, the national skills strategy, Department for Business Innovation and Skills. Nov 2009 (pp. 1-78). Retrieved from https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/228764/7641.pdf
BIS (2009a). Higher ambitions: The future of Universities in a knowledge economy, Department for Business Innovation and Skills. (pp.1-78).
DIUS (2008). A new ‘University Challenge’. Department for Innovation, Universities and Skills. (1-20).
QAA (2012). Enterprise and entrepreneurship education: Guidance for UK higher education providers
September 2012. Quality Assurance Agency. Retrieved from http://www.qaa.ac.uk/en/Publications/Documents/enterprise-entrepreneurship-guidance.pdf Page 1-32
Contact details: Dr E. J. Power, University of Huddersfield
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Lecture Theatre, Presentation Space
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
5Reflection and Action
7Communication and Strategy
In the working world, engineers are required to work with numerous stakeholders, from their own sector and from others, based locally, nationally and internationally. Engineering students will find themselves in many interview and presentation scenarios at the seek employments throughout their career, and clarity in communication will be essential in all areas of their professional practice. To that end, skills in public speaking, presenting and effective communication are essential.
An hour long session was run for a group of approximately 20 first year engineering students at Glyndwr University (studying on the Renewable Energy and Sustainable Technologies BEng programme), as an introduction to these skills, to be built on and consolidated throughout the rest of their time at the University.
The session formed part of a larger programme of guest speakers and practical workshops for the students, designed specifically to give the students skills for employability and self-employment, and a greater appreciation of the real world context for their studies. It was delivered by the University’s ZONE Enterprise Hub Manager, on the invitation of the course tutor.
(The session followed the format which can be found in the ‘Workshop - How to Speak in Public’ How-To Guide).

The students began the session with an introduction to the themes which would be covered, namely; how to structure a presentation, how to use tools effectively; how to present clearly; how to control and manage nerves, and how to deal with questions.
A brief discussion initiated the session, whereby students offered their thoughts on why public speaking skills were relevant in their sector, and how they might employ them in the future. From here, each of the themes above was covered in turn (with discussion following the pattern as outlined in the How to Guide).
At each stage, examples were chosen which were appropriate to the audience in hand. For example, in discussing structure and tools, a presentation on solar power was considered, and in discussing use of the appropriate language, thought was given to how an engineer would discuss the same technical point, with various expert and non-expert clients.
At the end of the one hour session, the key themes covered were re-capped, and students were offered the opportunity to ask questions, and directed to further support, links and reading if they wished to explore the issues further.
Though the session was limited to one hour only, it still made a valuable impact upon the students. Through initial discussions, students had a clear understanding of the purpose of the session, and its direct relevance and appropriateness to them.
As new undergraduates, many had limited experience of presentation and interview environments, and so the session was timely, giving a broad overview to key points, with clear direction on how to consolidate what was learned. However, the lasting impact of the session will be sustained if the students are offered continued opportunities to explore, hone and develop these skills in a variety of simulated and real-world environments.
Immediately after the session, students reported feeling more relaxed about public speaking, more confident, and better equipped going forward. Feedback comments included;
“Very useful”
“Very good. Gained knowledge to help for future presentations.”
“Really good presentation. Well structured, paced, and encouraged audience participation.”
“Good presentation on presentation.”
“Great presentation; well prepared, greatly delivered, well explained.”
“Very informative. Thank you!”
Resources:
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
For many years Business Plans have been considered as the main tool to encourage students to explore the opportunities for solutions to commercial problems. What has emerged from the work of Saras Sarasvathy, Steve Blank and many others (see references) is that planning comes before the Business Plan. Saras Sarasvathy has introduced the concept and approach to planning; Effectuation.
Practice with The Effectuation Approach makes the user more skilled and confident.
While it might be premature to hail the death of the Business Plan in undergraduate and post graduate curricula, we can certainly claim that its time is getting short. Thanks to the work of Alex Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, supported by Steve Blank and many others, the Business Model Canvas as a tool for planning has taken over in most curricula.
In addition, the work of Saras Sarasvathy and Colin Jones around how expert entrepreneurs actually behave and operate has led to the conceptual approach of Effectuation. Anna Kirketerp has combined a lot of the research into what makes successful entrepreneurs into her PUSH model (see references) which assists those of us in the teaching and learning space of Business Start-up.
However it is vital that students begin to practice how to use effectuation. This simple activity can get you started.
Using the ‘Saras Sarasvathy - What is Effectuation’ handout as a starter (see resources / references) discuss the key concepts and make sure that the group is clear on the principles. You can introduce the Saras Sarasvathy findings from successful entrepreneurs, or explore the Colin Jones “Resource Profile”.
The Resource Profile consists of three overlapping domains for each student/entrepreneur;
Students in small groups should compile their individual and then collective “Resource Profiles”. These will be unique complex and unexpected bundles of individuals, knowledge and information.
The task is for each small team to look to act as consultants to solve a unique problem.
The challenge is to come up with a proposal (as consultants) to a group of businesses who have decided that they want to create a new joint venture that they can exploit and grow their own existing businesses.
The facilitator/tutor then invites the group to select the three businesses that will join together to establish this new JV. This is achieved by the facilitator/tutor using an old fashioned Yellow Pages or Thompsons Local directory. Simply ask for three numbers between the first page and last page. (You can ask for three times (locations on a clock – to help locate more clearly on the directory page the chosen ventures/businesses). The three page numbers and locations on these pages will allow the facilitator / tutor to identify three businesses.
The facilitator/tutor then shares these business names with the group and invites the group to use “Effectuation” and their “Resource Profiles” to develop a Joint Venture for the businesses and to present their thoughts to the rest of the group at the end of the session.
I have used this activity with numerous groups of nascent entrepreneurs over the past few years. The idea is to force the students to realise that they bring more to the problem and potential solutions than their “Degree” and possibly “energy”. Serial entrepreneurs maximise the networks and contacts they have developed. Effectuation is the only way to create a new venture. Established businesses can use the theories taught on MBAs, Start-ups need to be fleet of foot and employ the principles of Effectuation if they are to survive.
At the end of the session the leaner will;
Appreciate that they are more than a single dimensioned individual – through the creation of their Resource Profile
Appreciate the power of Effectuation and its impact in business start-ups
Understand how to draw on the power of the team and each individual’s unique Resource Profile when working on shared problems.
Key authors: Saras Sarasvathy, Steve Blank, Alex Osterwalder
Further Reading;
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
I guess every class begins with an ice breaker. The cohort comes in anxious and uncertain and we typically want them to work collaboratively and in groups or teams. But how do we get the group into a learning zone and build the trust levels to ensure meaningful communication?
There will be as many ice breaking activities as there are tutors . . . so why am I adding this one?
I have used this with a variety of cohorts and built it into a wider activity – that of encouraging meaningful communication and learning. I link the simple game to a theory of communication and use the session to press home the key principles of communication.
Having demonstrated how we communicate instinctively, it is then easier to get the group to appreciate that how they communicate and how the level of their communication will determine how their collaborative work will benefit from a greater understanding of the level of communication within the group.
Hand out the “Human Bingo” sheet and invite the group to mingle and explore the group’s hidden talents.
Encourage rapid completion and reward lines, diagonals etc. with sweets (these always motivate – and Poundland do a brilliant range – though other retailers are also available!)
When you have had as much fun as you can cope with – invite the group to share what they have learnt about each other. While this wasn’t an initial objective – find out how much people listened to each other and who remembers interesting anecdotes. Listening and remembering is a key skill in communication!
Having been amazed by the brilliance of the group I typically move on to discuss the theory of communication and share the diagram from the “Leadership Trust”.

This simple model of communication is easily reinforced by examples and the group can be invited to share their experiences of the levels of communication.
The aim is to invite the group to identify how their emotions and the level of communication are linked. Can they recall examples of successful collaborative activities and identify the communication level the group were operating at to achieve the successful outcome?
If time permits, you can then move on to explore the level of a team’s development and how simple self-diagnostics can be used to establish the stages and what is required to move the group/team on (if that is what the team/group desire).
I started using this when teaching a Level 5 module that required the students to work on a difficult open ended problem. The task required high levels of trust and collaboration. It amazed me to see teams of “friends” who lived together and “drank” together – yet their level of communication was no greater than “ritual and cliché”. I decided that from then on I would begin every team building and programme requiring team work, with a session on communication.
I now use this with all the groups I work with – from under graduates to post graduates and experienced academics.
Understanding how we communicate and to have a language to describe it helps teams appreciate where they are and how to develop.
At the end of the session the participants will be able to;
If you would like to have your Case Study featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the Case Study.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
If you or your students are interested in developing a business idea, becoming self-employed/freelance or creating a business here are some tools to help and also some links to business start-up support.
These guides have been selected to build QAA (2018) entrepreneurship skills in your teaching.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Individual Task
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
Construct and deliver a focused and precise summary of their business proposal, that is attractive and engaging to a potential financer.
Prepare the entrepreneur for opportunities to present their business proposal, formally and informally, in a short space of time.
An ‘Elevator Pitch’ is a succinct summary of business opportunity for example, 1 minute or in no more than 300 words. The term is typically used in the context of an entrepreneur pitching an idea to a potential investor. This task invites the student to prepare for a minute pitch.
Invite the entrepreneur/small business owner to prepare a 3 minute pitch for their business The challenge for many entrepreneurs is how to describe their proposal in such a short space of time and what aspects of their business model and plan to focus on. A useful approach is to use Sahlman’s recommended four critical factors.
The People
Who’s involved?
What are their mission and aspirations?
What skills, know-how and experience do they have?
The Opportunity
What will the business sell?
Who are its customers?
What problem is it solving?
Why is it better than existing solutions (competition)?
The Context
What’s the bigger picture?
What trends e.g. economic, social, technological, political affect the business?
Risk and Rewards
What are the main risks?
How can they be mitigated?
What are the potential financial, and other, rewards?
Entrepreneurs/small business owners should be given time to prepare their pitch, either working independently at home or within a training programme. In a group situation this should take no more than 20 mins.
Entrepreneurs should then be invited to pitch their business with a strict time limit. This can be done in a number of ways depending on the environment, for example,
This activity helps the entrepreneur to focus how they think about their business and provides a safe environment in which to develop their communication and presentation skills, whilst refining their business pitch.
It can help the entrepreneur /small business owner effectively present their business proposal in both informal and unexpected situations and confidently to a potential financier. Repetition of this type of exercise builds confidence and expertise.
To provide formative experiences of pitching, before any assessment, you can create sub-groups within which the students pitch to each other, giving and receiving constructive criticism, before conducting the final presentation.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Individual Task
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
To develop an understanding of their capacity to undertake internationalisation as a way to grow their business.
Entering a foreign market could help your business reach new heights in terms of growth, revenue and longevity. This evaluation of a small business’s capabilities will reveal its potential for growth.
Instructions
Invite the entrepreneur / small business owner to consider the business from 3 perspectives to analyse their business’s ability to seize opportunities in foreign markets.
Organisational Structure Assessment & Actions
Does the small business have the structure and capability to expand?
Do the internationalisation plans contribute to and fit with the business mission and objectives?
Does the business model take internationalisation into consideration?
Are marketing and sales activities / plans in place to reach international markets?
Are products and services suitable for the international market?
Do they introduce innovation to the international market?
Does the small business staff team have the skills, knowledge and commitment to implement the internationalisation plans?
What actions are needed to support the internationalisation plans?
Financial HealthAssessment and Actions
Does the small business have the financial resources needed to support its international goals?
How much will the internationalisation activities cost?
Does the business have the cash / working capital to meet these costs?
Have alternative / additional sources of finance to internationalisation been explored?
Can the business afford to repay any debt incurred with international activities?
What actions are needed to support the internationalisation plans?
Leadership Assessment and Actions
Does the entrepreneur and their team have the commitment and understanding of what’s involved?
Is the entrepreneur or small business owner committed to internationalisation?
Do they have the support of their team?
Does the team have knowledge and experience of the international market?
Has advice been sought from experts and others with experience of internationalisation?
What actions are needed to support the internationalisation plans?
This activity draws together the key skills of an entrepreneur in terms of information handling and decision making. By using research skills and entrepreneurial effectiveness, this task invites the learner to determine actions based upon their own judgement.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
This session suits larger groups of learners being introduced to the concept of enterprise, creative thinking and solving complex challenges. Working with interdisciplinary groups works best to encourage maximum creativity and adds depth to the chosen solution. An introduction to effective engagement with audiences which moves beyond a pitch is introduced and the session closes with the audience crowd funding the idea using specially designed local currency.
This is best run over a 4-6 hour period and can be split between 2-3 sessions to allow for further research into the challenge. Session starts with some team building activities set firmly within the context of the challenge. This can help students to better appreciate the challenge area and develop empathy with various perspectives/realities in relation to the challenge.
Then follows some creativity exercises with an introduction to design thinking. Teams then apply this process (as time allows) through to completion with ideally prototypes being developed (if not posters/electronic adverts etc).
Then the large group is introduced to the need for effective and authentic engagement of themselves and their ideas (moving beyond the ‘pitch’). Individual or group presentations are developed and practiced. Depending on timing and group size, there can then follow a couple of rounds of presentations with a final selection presenting to the whole group. Ideally this should include at least one external stakeholder/s linked to the challenge context (clinical/engineering/finance etc) able to provide authentic feedback.
It can be fun then to introduce/revisit the concept of crowd funding and provide everyone in the audience with some currency (we have developed some university notes) and get them to fund their favourite proposal. Of course it could be that there will be some real funding available…
This works best with some facilitators to help support the various groups as they progress through each activity and often can make a significantly positive impact where groups from different curriculum areas meet for the first time. Utilising external stakeholders to share their challenges can also help to add real value and excitement for learners. Learners tend to enjoy the active nature of the workshop and the rigours of presenting to an external stakeholder with potential solutions to the challenges set.
Tend to see an increased awareness of wider enterprise and boost in confidence in terms of team working, design thinking, negotiation and engagement with audiences. A useful taster for deeper enterprising learning. Skilled reflection is vital throughout and post session/s through on-going programme. Depending on the nature of the ‘challenge’ this can be extended to a module/programme duration.
Brown, T (2008) Design Thinking, Harvard Business Review, June 2008 (pages 85 – 92)
Dweck, C (2006) Mindset: The New Psychology of Success, By Dweck, Carol S. ( Author ) Dec-26-2007 Paperback
Krueger, N.F.Jr. (2010) 13 Looking Forward, Looking Backward: From entrepreneurial Cognition to Neuroentrepreneurship in Acs, Z.K and Audretsch, D.B. (eds.), 2nd Edition of the Handbook of Entrepreneurship Research, Springer
Westfall, C (2012) The New Elevator Pitch: the definitive guide to persuasive communication in the digital age, Marie Street Press
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Lecture Theatre, Presentation Space
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
5Reflection and Action
A well-structured, well-research and well-written business plan is an invaluable asset to any new enterprise. Yet many students considering starting up report difficulty in developing business plans and in particular, plans which actively work for them and their business.
Business Planning is a workshop serving as an introduction to the subject, inclusive of opportunities to reflect on skills and generate ideas, and information regarding how to build a strong and cohesive plan around those ideas, and advice regarding using that plan, to turn those ideas into successful businesses.
The activity is designed to fit within a typical one hour lecture session, but inclusive of ample opportunities for extension, through practical activity, group discussion or independent research, and could easily form the basis of a more comprehensive scheme of work on the subject. It is designed to be appropriate for students of any level or programme of study. It was originally developed through the HEFCW funded pan-Wales Enterprise Support Programme.
Lesson plans and AV presentations for use in the delivery of the workshop can be downloaded via the link to the ‘ZONE Enterprise Hub’ webpages listed in ‘References’ and ‘Resources.’
The activity follows the structure outlined in the ‘Business Planning’ PowerPoint presentation, inclusive of all links and examples.

Figure 1. PowerPoint presentation which accompanies this activity.
Pre-Activity
Students are not required to prepare anything in advance of this workshop. For workshop leaders, preparation is minimal, other than ensuring supporting AV resources are displaying correctly.
Introduction
Why Bother?
What to think about?
What to write down?
Help and support
Students are provided with links and information regarding the support, advice and assistance available to them as they develop their business plans.
Conclusion
The key themes covered in the workshop are re-capped, and students are invited to ask any outstanding questions which they may have.
Post-Activity
This workshop is intended only as an introduction to the subject of Business Planning. Following the activity, students may utilise the information provided to research and develop their plans independently, or each element of the workshop may be revisited and explored in more depth by the group.
Students will leave the workshop with greater confidence in their ability, with a better understanding of their skills, and how these skills will support the development of their endeavours. They will have a better knowledge and understanding of business plans and how to develop them, and a greater awareness of how to use business plans to effectively support them in their endeavours.
Resources:
PowerPoint Slides accompanying this activity can be downloaded here > Business Planning [PDF]
Zone Enterprise Hub, Topic: ZONE Resources. 2015. [ONLINE] Available at: https://moodle.glyndwr.ac.uk/course/view.php?id=37§ion=11 . [Accessed 05 August 2015].
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Lecture Theatre, Presentation Space
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
7Communication and Strategy
This activity is designed to provide an opportunity for students to develop their understanding of the purpose and benefits of producing a business plan as well as expressing any concerns or issues relating to the process.
As an individual task – invite each student to consider the opposing statement below (that preparing a business plan is ‘a waste of time’ and ‘a valuable exercise’ and to make a list of the reasons why someone may agree with each of the statements.
Each point can then be researched, discussed in small groups, and challenged within the small group situation to create a consensus for presentation.
The activity should be concluded by asking the group to agree where they would rank themselves on the continuum and make their position to the wider group.
This will create a range of presentations, which will draw out of range of concerns and issues, that can then be discussed and explored across the wider group.
Preparing a Business Plan
A waste of time ...................................... A valuable exercise
0 10
This can also be repeated, following business planning work, to provide a useful reflection tool at the end of the business planning process, when students are invited to consider the statements again having completed the business plan. This can provide an indication of any change in the entrepreneur / small business owner’s view.
The decision making within this task is both individual and within a group and therefore develops consensus building through discussion and debate. The discussion will build deeper understanding of the business planning process and build confidence around this area, whilst the presentation skills to the wider group will build confidence in public speaking and debate.
If you would like to have your How to Guide featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the How to Guide.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
This case study describes a speed networking event that enables 1st years Computing and Business students to engage with Level 6 students in ‘live’ projects.
Level 4 student teams compete for business opportunities by attending a networking fair and engagement with level 6 students. The task is supported by in-class activities, but the emphasis is on learning by doing. Students are encouraged to reflect on the experience as part of the assessment strategy.
Participation at the event forms part of both year group’s module assessment. At the beginning of the academic year, final year student teams identify a year long project opportunity. They meet the client and develop a project to deliver to them. In the 2nd semester, Level 4 student teams are introduced to key concepts of business development and prepare to engage with Level 6 students at the speed networking event. In preparation for the event, Level 6 groups prepare project briefs. These briefs create a ‘mini’ market place for Level 4 groups to segment and target based on their own team goals. Typically, the students work in teams of four. After the Speed Networking event the teams from level 4 and 6 work together to complete their part of the project.
Specifically, students at level 4 prepare by developing an understanding of the start up business cycle. Such as team formation, start up strategy and product/ service development. Students are given prior knowledge of potential projects, which helps them target their pitch and brand. They learn to create rudimentary business artefacts such as a brand name; business cards and a sales pitch (see photo attachment). Students were also guided on networking skills, such as body language and professionalism.
Students at Level 6 prepare by developing a project plan with their project client. During the delivery phase of the project. They identify an outsourcing opportunity and produce a project brief, roughly 1 month in advance of the event. A pro-forma is provided to create a consistent look and feel to each teams brief, so that level 4 students can easily assess the merits of each potential project brief (see attachment). Around 20 projects are created by the cohort, which roughly matches the number of teams at level 4. The supply of projects can be increased by Level 6 students creating more than 1 outsourcing project. Projects range from simple tasks, such as logo design to more complex projects, such as research, web development, and media production.
The project clients are typically from external organisations, such as charities and local businesses, but can be internal clients, such as, as tutors. Project size for level 6 students should be complex enough too ensure that the challenge provides adequate work for each team member. The sub task project for Level 4 can be relatively simple. It is more essential to engender confidence and good team work at Level 4.
The competitive nature of the event means that teams are not guaranteed to get what they want. Success is often determined by the quality of planning carried out in advance of the fair, or by the professionalism of the team on the day.
The event is very popular and student engagement in the event is close to 100%, with around 150 participants. While conducting the task, students have very little time to become distracted, which means that they receive the full benefit of the session.

Student feedback comments are also very positive:
Verbal and scored Feedback

National Student Survey feedback comments single out the modules as a key benefit from the course.
“I really enjoy this course, as it's stimulating and pushes my boundaries. I have noticed vast improvements in my abilities, in terms of communication, presenting and teamwork. All staff are very helpful in terms of problem solving and it's nice to know that the support is there when needed. I enjoy the course content and how interactive the course is.” NSS 2015
“The course really targets employability and it really appeals to employers that we gain hands-on business skills.” NSS 2015

Students learn the benefit of planning and preparation. They also understand that it is difficult to communicate in a time pressured environment. An interesting side effect of the event, is that students in level 4 can benefit from a peer mentoring experience; learn about the course and how to be successful at gaining a placement. The event is also a novel learning experience and adds a new dimension to the university experience. Final year students benefit from the reflection of ‘how they used to be’, which adds to their confidence.


Contact details: Dr Andrew Hirst, Teaching Fellow in Work Based Learning, Sheffield Hallam University https://www.linkedin.com/in/drandrewhirst
If you would like to have your Case Study featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the Case Study.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
Cases Studies of Good Practice can be found in Higher Education Academy booklet (2014) Enhancing Employability through Enterprise Education Case Studies and includes an example from the School of Computing and Engineering at University of Huddersfield.
This 3 day event 'The Enterprising Engineer' designed to be of equal benefit to students intending to enter university and students intending to start up their own business, may also be of interest.
In addition Enterprise Educators UK (EEUK) publish case studies that demonstrate the impact of their enterprise and entrepreneurship education from their members, including "Formation Zone" from Plymouth University.
Business Start-Up Resources
BOSS stands for the Business Online Support Service, provided by Business Wales. This service provides online learning courses to help people who are thinking about, or actually, starting a business, already running a business or looking to grow their business.
Big Ideas Wales The Big Ideas Wales campaign is part of the Business Wales service, designed to support the next generation of young entrepreneurs in Wales.
Nesta Creative Enterprise Toolkit
Our enterprise resource toolkit contains tried and tested methods for teaching enterprise skills to creative individuals who are thinking about setting up a business. Available for purchase - with access to resources here http://www.nesta.org.uk/sites/default/files/cet_worksheets_case_studies_and_tutor_notes.pdf