Enhance your curriculum by addressing the QAA Guidance on skills for your subject, and incorporating the QAA (2018) Guidance on Enterprise and Entrepreneurship.
The following ETC tools can help you to deliver these skills in the curriculum
These guides have been selected to build QAA (2018) enterprise skills in your teaching.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Presentation Space, Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
5Reflection and Action
7Communication and Strategy
The focus within this task is to stimulate team building and decision making through the research process.
Within this task, students will work together to explain their findings to group peers as they understand them and progress the plan as a group. (Some students may later undertake a summer studentship so they have been prepared for the situation as a result of this authentic assessment).
This task was based in Microbiology but would be accessible to any discipline where a research strategy and resources are required.
By placing the students into groups, issue the aims and introduction from a real research studentship (available from HEIs or via colleagues) and issue the task to design the activities required for the eight week research summer project.
This challenge is complex for the groups to address and requires them to utilise peer learning to understand what is required. Your role as tutor can beadjusted, depending upon the needs of the group, but it is suggested that you present yourself as a ‘resource’ to their learning, rather than ‘the guide to’ their learning.
You may wish to include regular contact time which could involve:
Students prepare a one page summary on their approach and what part of the project they researched. They also present their group studentship plan as a short group presentation (10 mins). Questions and comments from other groups should be welcomed, with the aim of enhancing their approach and improving their work through this final opportunity for peer-review and tutor comment.
This task helps the students develop the mind-set of a researcher; questioning why and how for each experiment, and evaluating feasibility with respect to cost and time. Usually students would not develop these skills until postgraduate studies level so this encourages students to develop key skills early (so they may be utilised or referred to in an employability context).
Key skills include
However it is important that you draw out this learning within their presentation or within a final group discussion. It might also be helpful to review the ‘changed’ role of you as tutor, in directing the journey of their learning, and providing opportunities for review and enhancements, rather than immediately resolving their problems.
You can also explore with the groups how the decisions were made and resources accessed, exploring social networks as well as traditional academic resources (Guides; texts etc). Those that contacted senior researchers or their subject club/society may have drawn on expertise and experience and thisproject encourages them to access support as widely as needed. It also gives the opportunity to review and evaluate sources, and comment upon the validity of different materials.
Flat floor teaching space with tables so students can engage in teamwork activities
Quick teambuilding games: re-ordering a sequence of events, contingency planning, structuring research, and decision making
Enterprise for Life Scientists; Developing Innovation and Entrepreneurship in the Biosciences. Adams. D.J, and Sparrow. J. (2008). Scion
Research scholarships information page (2015) www.ncl.ac.uk/students/wellbeing/finance/funding/ukstudents/vacation/
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Presentation Space, Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
This is a two hour session and it will begin abruptly by creating a case study with the student group.
The idea is to pick on a student and announce in 5 years' time "Jane"(or John) will run a successful arts consultancy. This will raise some surprised gasps and giggles which will immediately engage students' attention. The narrative that unfolds will demonstrate: how Jane started out in one direction but discovered, and followed, opportunities elsewhere, how she took a few risks, showed resilience in the face of setbacks and how she turned to her networks (other students in the room who come into the story) to help her fill skills gaps and capacity problems.
The case study is pre prepared and can be tailored to the cohort. It should be approximately 10 mins long and the story should be plausible – not extraordinary – a case of everyday entrepreneurship. It will be fun as it draws the students into a fictional story.
Following this there is a 30 min breakout to discuss in groups of 3 or 4 to analyse Jane / John's journey: how did he do it, the key factors for success, would you have done it differently, could you have done the same journey, have you encountered any similar situations to John, if so what did you do? Students post thoughts on stickies.
The management of feedback here is important because the students, who are reluctant entrepreneurs, should be led to the explanation that this behaviour is entrepreneurial. The session is to not only identify the behaviour as entrepreneurial but to get the students to reflect on their experiences in similar situations and imagine how they would respond. The idea is for the students to see enterprise as tangible, every day (familiar even), as a series of minor steps and small scale risks and about trying things out to see what happens.
The upshot of the feedback session is that the students 'discover' the entrepreneurial mind-set for themselves – they have not listened to an expert talk about it for 50 mins – and that they identify with it as something they can do themselves.
The session finishes with 10-15 mins reflection where students have to pledge to do something entrepreneurial that week. It could be something they had been thinking about for a while but had made excuses not to do it. Others may need a little help and guidance from peers about what they might do, so reflection and pledge setting should be discussed in groups. The follow up session (if appropriate) will be when more detailed reflections can emerge and when students can get a measure of where they might be regarding their own development in terms of entrepreneurship and the enterprising mind-set.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
Effective engagement of Alumni seeks to support the students to become:
With the pre-arranged (and prolonged) support of alumni (now professionals) this approach of continued access to external professionals (ideally programme/course Alumni) is designed to prepare students to be able to engage with real clients and better enable them to respond proactively to change.
Externals are invited to engage with the current student group as they undertake a task, using social media (facebook; twitter etc) an/or Skype. This creates either incremental weekly instruction that builds into an overall assignment or regular support or feedback on course work from externals.
This approach needs pre-agreement and commitment of externals (ideally Programme/course Alumni) who commit to short, but regular interaction through social media or Skype.
This activity can either be driven by a live brief or challenge identified by the external (higher level of engagement) or as comment and support to those undertaking the programme, through sharing expertise and current work experiences. If the students are working on a live brief or task given by the external, this high level of interactivity can mean that summative deadlines can changedand information updated, and the newsworthy or other high profile influences can be included throughout the module. (The assignment usually mirrors an actual assignment undertaken professionally by an Alumni professional).
This engagement can be “managed” by the tutor – to pre-plan some ambiguity or pre-agreed change of brief/scope with the Alumni contact, or left open to allow access to externals as an organic relationship, where advice may be sought by the students or experience/daily practice shared by the Professional as they see fit.
In addition, any presentation /show case or final assignment submission can be shared with the external and their input made part of the summative or formative feedback (assessment strategy).
Note that the choice of social media will impact on the type of engagement between alumni and students, but ideally something that the Alumni member uses regularly will ensure more regular engagement. Even small inputs (as typically seen in social media such as Twitter) can guide student approach and ensure that they are able to ask private questions, and that other students can also learn from the mentor/alumni generic comments or insights.
Depending upon the level and type of engagement, students can benefit from insights from a ‘typical day/week’ of a professional working in their area, or be pushed to develop their tolerance to ambiguity (through changing deadlines, or unexpected changes to the brief or additional information). This can build resilience in the students but there needs to be clear expectations of this relationship, as well as additional tutor support.
Students typically respond well to changes and additional insights from professional Alumni and can develop their understanding and judgement, in their chosen field, whilst gaining further insight regarding professional practice.
Students should be bought together to share their experience of virtually engaging with their Alumni contact and explore their emotional responses to the changing briefs or additional information. They need to explore, and develop strategies, for coping with ‘real world’ brief/challenges and exploringthis together, and sharing how they dealt with it, and could deal with it in the future, builds their confidence and resilience to change. Using reflective practice to consider the learning across the group can draw out a range of key lessons for preparing for future challenges.
Access to, and ongoing (committed) virtual engagement by appropriate alumni – determine brief/project or to commit to regular updating/comment for a pre-agreed period of time.
Penaluna, A., Penaluna, K and Diego, I. (2014) The role of education in enterprising creativity. In Sternberg R and Krauss, G. (2014) Handbook of Research on Entrepreneurship and Creativity. Cheltenham / Massachusetts: Edward Elgar).
Scott, J., Penaluna, A., Thompson, J & Brooksbank, D. Experiential entrepreneurship education: Effectiveness and learning outcomes. International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour and Research (Forthcoming)
Jones, C., Penaluna, A., Matlay, H., Penaluna, K. Discovering the Soul of Enterprise Education. Education +Training, Emerald Publishing (Forthcoming)
Penaluna, K., Penaluna, A., Jones, C. and Matlay, H. (2014) ‘When did you last predict a good idea?: Exploring the case of assessing creativity through learning outcomes’, Industry and Higher Education, Vol.8, No.6, December 2014: 399 - 410
Penaluna, A., Coates J. and Penaluna K., (2011) Creativity-Based Assessment and Neural Understandings: A Discussion and Case Study Analysis. Education + Training, Emerald Publishing, Volume 52, Issue 8/9, pp. 660 - 678
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Outside
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
This exercise is a fantastic way to get people working together as they tackle up to 10 tasks in a given time frame. With limited information (on each other and the tasks presented) the group must navigate through the challenges in order to be the most successful group (back within the time frame; most tasks achieved; most accurate delivery of the tasks). Depending on the tasks selected, specific industry or sector knowledge can be tested as widerskills of background knowledge, research and creative thinking are required. Insist upon evidence of the achievements (photos on flip or camera phones) as well as delivery of objectives.
Activity : This activity needs a long session (such as 120 minutes) to complete, reflection and analysis takes place at the end of the session.
The groups of up to 6 people are sent out to complete > 10 tasks (usually 3 cryptic, 3 researched and 4 fun)
Examples of these could include:
These tasks should be developed beforehand to suit the environment where the day is taking place. Ensure there are fun tasks involved and that everyone has a chance to engage by creating a range of challenges that involve the physical, mental, social aspects of your learners.
To manage this challenge effectively, if it important that you:
Practically it can also be helpful to give them a puzzle to solve before they can leave and a further one when they return. This means they are leaving at different times and they return to a final challenge, so that you can record time and award points.
Depending upon the challenges you create, there is a wide range of transferable skills and knowledge base that you can test during this challenge. You can create tasks that draw upon their:
It is important that you review the challenges and how the groups tackled the tasks in order to draw out the subject learning and these wider skills, before reviewing the wider team experience by exploring:
Drawing out the team dynamics will allow the students to identify the lessons that they can take forward that will improve their future group work and learning experiences.
Ask if they started by sharing their knowledge and skill set or just started on the tasks (the most typical response) and whether they would do that again. Ask when, or if they ever start a task by reviewing when they have collectively or individually undertaken something similar and what was learnt that they could take forward.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Presentation Space
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
7Communication and Strategy
This physical task engages the whole person in supporting a colleague and ensuring their safety through good communication. The activity can be used at any time during the session, however it is highly effective as and ice breaker. It is a fun method to start participants communicating and is simple to deliver in an appropriate environment and can be adjusted depending upon group size, age etc. However health and safety is paramount and you must consider the appropriateness of the group and room for this challenge.
You should initiative this activity by stressing the nature of the challenge and stressing that the safety of those involved is paramount. You can also agree across the group that “stop” can be initiated by any member of the team by raising a hand if they don’t feel that it is safe to proceed. This can be actioned by anyone and will not result in any penalties.
To run the task, gather the group outside the room and:
It could also be possible to create a preferred route or course (as seen in horse show jumping) which they need to accomplish (if you didn’t wish to use obstacles for safety or mobility reasons) which would lead the pair to particular numbers/letters indicated on the wall.
Subject specialisms could also be tested by placing knowledge based answers on the walls and asking the pairs to walk to their answer through the course (see QAARunaround for details of how to do a multiple choice but don’t mix the games in play for safety reasons).
This task requires listening and communication skills and also helps builds trust and connections across the pairings. However the skill development and improved future practice comes from evaluating performance across the group and understanding how and when particular techniques were effective and what lessons that provides for the future. It is important to acknowledge fears and concerns, or frustrations between the pairings but keep the discussion to the general learning, rather than focusing upon particular experiences of individual pairings as the depth of learning will come from the lessons that can be applied in future group work or communication challenges. These lessons include clear communication; agreeing ground rules for working together; recognising the need of feedback or support; understanding the importance of clear short messages within these circumstances etc.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Presentation Space, Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
After participating in this exercise, learners should be better-able to:
The task is for groups of learners to make a container to hold an egg that is capable of being dropped from a specified height and position in the room without the egg breaking. To do this properly you need about two hours in a large flat room, big enough to enable groups to work independently. This is a practice task to familiarise learners with the concepts of meaningful assessment criteria, weighting and agency of assessment and is particularly useful during the first six weeks of the first semester of the first year. It is presented as serious fun which improves learners’ assessment literacy. It’s also a good staff development exercise to get staff to think hard about assessment issues.
Learners in a class (16-70) are divided into groups of 4-6, at separate tables around the room, and provided with a range of everyday objects as resources, including an unbroken fresh egg. They are briefed to use the resources in a specified time to arrange that the egg can be dropped from a specified height and position in the room to ground level, and remain unbroken by the fall. They are to use the various resources in a creative way to achieve this. But first the groups must come up with around five assessment criteria, which will be used by the other groups to assess each group’s achievement of the exercise, and the whole group of learners must assign weightings to each of the criteria. One criterion is not negotiable: “The egg remains unbroken by the fall”.
Flipchart of white board to display agreed assessment criteria.
Supermarket carrier bag, per group, in which you place:
It is important that each bag contains more-or-less identical kit, otherwise appeals of ‘unfairness of assessment’ may arise (though of course you might wish this to be one of the matters which will arise, in which case allow some differences in the kit).
If you would like to have your How to Guide featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the How to Guide.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6)
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Carousel Tables (small working group)
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
It goes without saying that networking is a really important activity. Yet students are often reluctant to engage in relationships beyond their immediatecircle. They have powerful aversions to networking partly based upon fears and misconceptions about what it is: selling (it’s all about selling yourself and pitching), that it is about being an extrovert (sociable and bubbly), that they as students have nothing to offer (‘who would want to talk to me?’), that it seems pointless (students will have stories about going to events collecting business cards and nothing ever happening). They will have a multitude of good reasons why they can’t and shouldn’t do it. The challenge is to turn round these misconceptions and show students that networking is valuable, doable and indeed enjoyable.
This activity has been delivered with 3rd year Design and Visual Arts student, 2nd year Photography students and MA Contemporary Art students at Coventry University.
The first task is to get the misconception and fears about networking out into the open and to introduce different versions of what networking might be. This can’t be done by asking students about their fears and why they don’t currently engage in networking: this is sensitive and students may feel embarrassed talking about it.
The session begins with the value of networks and networking. This should be interactive, talking to students about their networks, how they found opportunities, but also using statistics about how many jobs are filled via networks rather than open advertising. This part of the session functions as a warm up and should get students feeling positive about networking.
The second activity is to get them into groups and ask them to draw a ‘good’ networker. This will bring out some of the negative misconceptions about it:students will draw someone who is extroverted, experienced, knowledgeable, valuable, confident, good at pitching – all the things they may not be good at. This is your opportunity to demonstrate that a good networker is someone who is good at listening, (not talking), it is someone who is genuine and open (rather than focussed on their own agenda) and that it is about building trust and rapport leading to a lasting relationship. It’s an opportunity todiscuss their value as students – which they are very anxious about as they have little work experience. Here a discussion about their value in terms of innovation, fresh thinking, new ways of doing things is important.
The third activity is a group brainstorm around how to create rapport with someone: suggestions will include, smiling, shaking hands, complementing people, being helpful, listening to what people have to say. This section could include a listening activity, for example where individuals have to listen to partners and paraphrase.
The final session involves practical activity. The students will network amongst themselves. It’s important that they shake hands here: this is partly about creating the rapport, discussed earlier, but also about adopting a more professional outlook and attitude. The students will find this both fun and challenging and some students will become anxious about it so it is worth doing a bit of role play to try it out: i.e. demonstrations of how to shake hands and introduce yourself. The result is that students will feel more professional
The assignment is:
Find a person, introduce yourself: impress upon them your integrity and openness
Reflect on what you did and report: One positive technique; One negative technique
The feedback will draw out feelings about handshaking, observations about body language, about personalising conversations by using the other person’s name.
Students’ misconceptions about networking are reversed.
They feel more comfortable with the idea of networking – they thought it was all about sales and the pitch but find it is actually something they could do. Some students struggle with the handshake, they find it very unusual but with a bit of practice and shift in attitude, do get it.
A group of students who know one another is not as good as a mixed group where they might be introducing themselves to strangers. However, the practical element can be modified by asking students to find out something new about their colleagues, or to find out a shared interest they didn’t know they had with a colleague which will help build rapport.
Students understand the networking is a skill that they can practice and develop. They learn the importance of networks and collaboration. They learn that networking and professionalism is a ‘performance’ which they can adopt when necessary – in this context it can be useful to talk about wearing different hats as they often think of themselves as ‘students’ which can carry a lot of negative connotations.
Classroom and tables
Key authors
Books
Links
www.
www.
www.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
Objective:
‘Renewable Energy Enterprise and Management (REEM) is a unique multi-disciplinary course blending appropriate project evaluation techniques and business enterprise with awareness of the potential of renewable energy technologies. The distinctive flexible learning approach blends distance learning with intensive face-to-face weeks on campus.’
(http://www.ncl.ac.uk/postgraduate/courses/degrees/reem-msc-pgdip-pgcert/#profile)
Introduction:
Katie Wray, Lecturer in Enterprise, Newcastle University;
“In Renewable Energy there are 2 MSc options at Newcastle University, MSc Renewable Energy, Enterprise and Management (REEM) and Renewable Energy Flexible Programme (REFLEX). REFLEX is for applicants that have a hard engineering first degree: REEM is open to students from a wide range of technical and non-technical backgrounds.
Activity:
“REEM is structured as a year-long programme made up of block teaching weeks (10 credits = 1 full week of teaching plus a pre- and/or post- school assessment). The programme introduces enterprise and entrepreneurship as shown in red below.
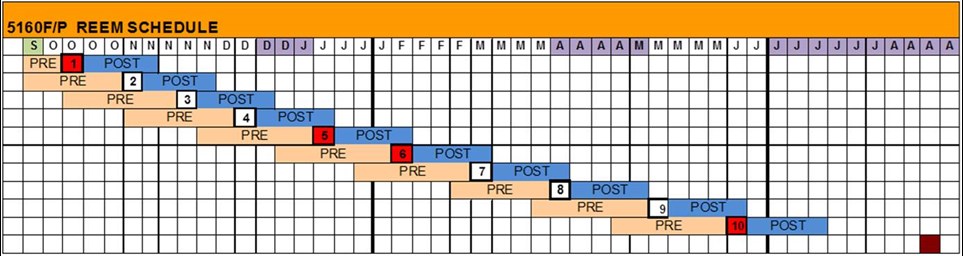
Figure 1
“This gives the foundations at the beginning and end of each semester to ensure that the theme of enterprise and the application of the technical, project and policy modules is reinforced throughout.
“Students undertake practical enterprise training during these modules as well as undertaking an Enterprise Project dissertation, in which they undertake a business plan or feasibility study into a new opportunity for renewable energy.
“By teaching in a block week format, it is possible to simulate a boot-camp style learning experience during an intensive week, and to build good peer relationships which would otherwise not be possible outside the classroom. Some examples of the topics covered in the 2 modules are shown below.
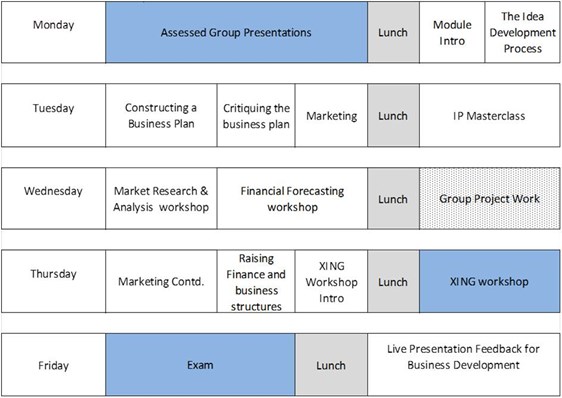
Figure 2: SPG8015: Introduction to Enterprise and Entrepreneurship in Science and Engineering

Figure 3: SPG8016: Business Enterprise in Science and Engineering
Impact:
“The students have independently created an interest group for both REEM and REFLEX (started by someone on REFLEX) for students that are interested in enterprise and entrepreneurship. The group is like an informal society. It is based on opportunities emerging in Renewable Energy or Energy Management.
We see students applying for these programmes do so because they have identified some growth opportunities in the sector.”
Learner outcome:
These examples of curriculum development for enterprise related outcomes were originally outlined by Neil Coles at the International Enterprise Educators Conference under the heading 'From Archaeology to Zoology; an A-Z of enterprise in the curriculum'. For his work in contextualising enterprise for any subject, Neil won the 2013 National Enterprise Educator Award.
References:
If you would like to have your Case Study featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the Case Study.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
If you or your students are interested in developing a business idea, becoming self-employed/freelance or creating a business here are some tools to help and also some links to business start-up support.
These guides have been selected to build QAA (2018) entrepreneurship skills in your teaching.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5Reflection and Action
6Interpersonal Skills
7Communication and Strategy
Each year an institution and region wide Business Idea Competition is run as a broad tool to stimulate and support entrepreneurship in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. The competition promotes creative thinking and problem solving for learners at all stages of the learning journey including upon graduation. Our institution comprises a network of tertiary colleges and research centres, spread across the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. The competition was devised and is organised by Create, an Enterprise and Innovation Learning centre based within Inverness College UHI and delivered across the university and all partner institutions including the surrounding Highlands and Islands community (subject to T&Cs).
The competition is supported across campus to significantly raise ‘Enterprise Awareness’ (via induction, workshops, talks, e-comms), develop ‘Entrepreneurial Mindset’ (through intensive engagement and support to submit entries to the competition with learners from all faculties) and for some students (who progress in the competition and beyond) to start to develop their ‘Entrepreneurial Capabilities’. We have examples of this being delivered as an extra curricula workshop/activity and within the curriculum as a tool to aid experiential learning.
The competition opens in August each year and is promoted widely across the university, all colleges and research centres and in the local community. Lecture ‘shouts’ and workshops have proven to be the most effective technique to engage the broadest range of staff and learners. Short films are included on our website to give tips on entering.
Online entries seek information on an idea, inspiration, resources, next steps rather than a business plan. It was inspired by the culturally popular ‘Dragons Den’ but was dubbed the friendly ‘Highland Dragons Den’. Plenty of support is provided for developing application, pitching and presenting. Independent and experienced judges are engaged each year and relevant follow-up support and advice is offered to all entrants. For winning entrants, start-up support is offered in addition to cash prizes.
CREATE has worked closely with regional partners and the business community to ensure the competition reaches the maximum potential budding entrepreneurs across the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. The competition was launched in 2006 with 27 entrants and has grown significantly to 150 entrants in 2014 representing all industry sectors and parts of the region. Subsequent business start-ups in both the commercial and social sector have proved to be a recognised economic benefit to the region.
In addition to business start-up, it is considered that the competition also has two key impacts: it significantly enhances ‘Enterprise Awareness’ across curricula areas (both academic/careers staff and students); and helps to encourage stronger working relationships with local business and enterprise support organisations.
This activity shows how education ‘for’ enterprise can successfully engage a wide range of students, staff and members of the community both within and outside the curriculum. Over the years, more teaching and career staff are building in this opportunity as an awareness raising and experiential tool for learners at all levels. Those who participate, are extremely positive about the experience and can articulate evidence of creative thinking, opportunity spotting, and business awareness and, for those who proceed in the competition, they are able to develop their presentation, commercial awareness and network building skills. They talk of an increase in confidence and greater awareness of ‘know who’ and ‘be known’. Through CPD sessions, more academic staff now have the confidence to introduce these concepts and encourage learners to try this opportunity ‘to make something happen’ which adds to a student’s experience of how it ‘feels’ to be enterprising, which is very much in tune with the philosophy of enterprise education.
For 2015/6, we are extending the competition to early stage start-ups as we find many entrepreneurs start to test their idea earlier each year and still benefit from this type of engagement and encouragement.
Partnership: A critical success factor for this type of region wide initiative is partnership working. Within the institution, we engage with Deans, Faculty and Subject Leaders as well as Careers and Student Services areas.
Externally, this initiative has helped to build strong working partnerships which have grown year on year with local enterprise support organisations (Business Gateway, Prince’s Trust Youth Business Scotland, HISEZ, FirstPort and SIE) together with an extensive range of regional businesses (large corporates and SMEs) who wish to be associated with helping to build a vibrant entrepreneurial culture.
Funding: The activity has been substantially funded by institutional funding with support in the early years from the local enterprise agency, latterly EU funding sources and local council funds. All prizes (£8,000 in 2015) are sourced via sponsorship from local business and enterprise support organisations which CREATE attracts each year.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Small group (teams of 4-6), Large Group
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Carousel Tables (small working group), Special
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
1Creativity and Innovation
5Reflection and Action
7Communication and Strategy
Rocket pitches or elevator pitches are often the first opportunity for an entrepreneur to convince potential investors that they have an idea that represents a profitable opportunity. These are often only one to five minute presentations, but they can have a significant impact on the entrepreneur’s ability to attract investors as well as other potential stakeholders. This can be particularly true in the early stages of a venture before the entrepreneur has a viable product, and he or she has to quickly convince potential stakeholders of his or her vision and the potential of the idea. Entrepreneurs often think that their idea is the most important aspect of the pitch, but studies have shown that U.S. venture capitalists consider personal characteristics such as the entrepreneur’s ability to articulate his or her venture to be critical in determining whether or not they will reject an entrepreneur’s plan.
In this exercise, students design a paper airplane that must be capable of carrying a predetermined amount of currency in the form of coins. The airplanes will compete in two categories – time that the plane can stay aloft and the distance it can travel. However, students pitch their design to their classmates (the investors) in an effort to convince them their design is the best before the contest takes place.
The exercise has worked well for illustrating the importance of a good pitch and helps students to better understand what constitutes a good pitch from an investor’s perspective.
Usage Suggestions
This exercise works with both undergraduate and graduate students. It is appropriate for new venture creation courses, entrepreneurship boot-camps, or workshops. The session is best positioned after students have identified a venture concept, project, or family or corporate initiative to pursue and are preparing for an elevator speech or rocket pitch type presentation. Technology entrepreneurship or innovation classes are also appropriate.
Pre- Work Required by Students
Students are to be given the following instructions in the class period prior to running the exercise: “You are to design and create a new paper airplane capable of keeping one U.S. dollar of coins aloft for as long (time) as possible while simultaneously transporting the coins as far (distance) as possible. The assignment is as follows:
You will be required to pitch your design to your classmates. You will have two minutes to convince your classmates that your design will perform the best. Performance on the exercise will be based on a combination of actual performance of your airplane and the number of votes your design gets from your classmates in each category (time and distance).”
Time Plan (80 minutes)
Because each team will pitch their idea, the time required for the exercise will vary with class and team size. The timing outlined here is based on a class size of 30 students and ten teams.
Step 1 0:00–0:02 (2 minutes)
Begin the exercise by explaining the voting rules to the students. Students are allowed to vote for only one team (excluding their own) in each of the two categories (distance and time). They are not required to vote for the same design in each category. It helps to provide a sheet for each of the students to record their votes, or, if your students have computers and internet access, you can use an online voting system (this will require you to set it up before the class).
Step 2 0:02–0:27 (25 minutes)
Next, have each team pitch their idea to their classmates. Teams should be strictly limited to two minutes each.
Step 3 0:27–0:32 (5 minutes)
Have the students record their votes for the design they think will perform best in each category. Remind them that they cannot vote for their own design.
Step 4 0:32–0:52 (20 minutes)
Take the class to an open area in which to conduct the actual flights. An indoor area such as a gymnasium works best, but you can run it outdoors as well (which can introduce additional uncertainty into the performance for the students). Each team gets one throw. You should have a line that they cannot cross for throwing, and you should record the time that their plane stays aloft. After the plane has landed, measure and record the distance. It helps if you assign this task to one or more of the students.
Step 5 0:52–1:00 (8 minutes)
Return to the classroom. Record the votes and the actual performance for each team on the board.
Step 6 (exercise debrief) 1:00–1:20 (20 minutes)
If time allows, you can have a short discussion about their process with regard to creating their design. This can help to illustrate how an entrepreneur can take a constraint and turn it into an opportunity. Additionally, this can highlight the importance of prototyping and learning from failure, and many of the teams that perform well often trial several different designs. Some possible questions include:
Next, discuss the aspect of effective pitching. The idea here is to get them to appreciate the importance of the entrepreneur and his or her pitch to investors. Owing to the uncertainty inherent in many early- stage entrepreneurial ventures, investors will typically put more emphasis on the entrepreneur and his or her ability to “sell” the idea, as well as their confidence in the entrepreneur’s ability to execute on his or her pitch – one has to be careful not to oversell the concept.
Wrap the discussion up with a summary of the importance of clearly articulating your idea and convincing the audience of your ability to execute on your idea.
Post- Work
Have the students read the following articles (this can be done beforehand if you prefer):
Teaching Tips
Students will often try to game the system (depending on how much freedom you give them). For example, they may choose to use different weights of paper or design a flying disc as opposed to a traditional airplane. You can decide how vague you want to be. If you want to have more discussion on the creative process and pushing the boundaries, then being more vague in the instructions can lead to a good discussion on how entrepreneurs try to push the rules and boundaries. Some students will feel “cheated,” but this can still provide a good learning point.
Key Takeaways
Materials List
Provide students with paper for their airplanes in order to maintain a standard paper type and weight. Alternatively, you can leave this open to interpretation as a means of encouraging greater creativity among the teams. You will need a tape measure and a stopwatch for the actual competition.
The full text ‘Teaching Entrepreneurship: A Practice-Based Approach’ can be purchased here > http://www.amazon.co.uk/Teaching-Entrepreneurship-A-Practice-Based-Approach/dp/1782540695
This exercise is taken from;
Attribution
Theoretical Foundations
MacMillan, I.C., Siegel, R., and Subba Narisimha, P.N. 1985. Criteria used by venture capitalists to evaluate new venture proposals. Journal of Business Venturing, 1, 119–28.
Ries, E. 2011. The Lean Startup: How Today’s Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses. New York: Crown Publishing.
Group Size
?
1.) Small group (teams of 4-6)
2.) Individual Task
3.) Large Group
4.) Any
Any
Learning Environment
?
1.) Lecture Theatre
2.) Presentation Space
3.) Carousel Tables (small working group)
4.) Any
5.) Outside
6.) Special
Any
QAA Enterprise Theme(s)
?
1.) Creativity and Innovation
2.) Opportunity recognition, creation and evaluation
3.) Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4.) Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
5.) Reflection and Action
6.) Interpersonal Skills
7.) Communication and Strategy
8.) Digital and Data Skills
2Opportunity recognition‚ creation and evaluation
3Decision making supported by critical analysis and judgement
4Implementation of ideas through leadership and management
7Communication and Strategy
This type of module is appropriate on applied courses, or courses ‘with enterprise’. It is especially valuable where students from a range of disciplines are taught together, invited to ‘bring their discipline and interests with them’ (of course, discipline and interests are not always/often synonymous, and this approach helps with that!)
Students engage in a shared first lecture, setting the context for the module, discussing, and responding to individual learner expectations, and an introduction to innovation, delivered by an inventor, which asks the students to invest in one of a series of inventions, based on a case study of each in practice. They are encouraged to reflect on their choice, and in particular the reasons why they feel that their chosen option represents most value.
In week 2 students return to their own discipline (or choose an area of interest based on the available disciplines) and a session is led by academics and industry guests/entrepreneurs focussing on ‘the current and future trends in the XYZ industry’. This tends to be ‘products for users in Science and Engineering’ subjects (e.g. pets and children), and ‘approaches’ in other subjects (e.g. social and online media).
Week 3 is a facilitated session in which students join interdisciplinary groups (formulated with as wide a variety of disciplines as possible (e.g. 1xcomputing science, 1xbiology, 1xmarketing and management) and share their findings from the previous week to identify areas of shared interest and the skills each member can contribute.
The remainder of the sessions are built around convincing the module assessors, and industry/entrepreneurs that your emerging idea is worth spending more time, money and effort on developing, and that individual students have the appropriate skills and motivations to deliver on the opportunity. The design of the remaining sessions is aimed at students achieving this objective. Remaining module content and tools can be designed together with the students, using flipped classroom, online resources, and update meetings alongside taught lecture material.
The confidence gained by the students is seen as they engage with each other and with externals (industry experts). They are exposed to entrepreneurship through opportunity spotting and evaluation, and through building their reflective and persuasive/selling skills. By working in teams they are building collaborative approaches to problem solving and task completion.
Planned engagement – including engagement of academics, entrepreneurs and industry partners in each discipline where a student originates.
Time to coach groups individually, access to mentors or online interaction.
If you would like to have your How to Guide featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the How to Guide.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
If you would like to have your Case Study featured, please download the template and email the completed version to hello@etctoolkit.org.uk.
We have produced a guidance sheet which will assist you in completing the Case Study.
If you have any questions regarding completing the template, please Contact Us.
was developed through the HEA GEES Subject Centre project run in 2005. It is a collection of information, ideas, examples of practice and case studies which is intended to provide a starting point for those interested in including elements of enterprise/entrepreneurship within their modules or courses in geography, earth or environmental sciences. It can be found through the HEA website
https://www.heacademy.ac.uk/resource/enterprise-skills-and-entrepreneurship-resource-pack
can be found in Higher Education Academy booklet (2014) Enhancing Employability through Enterprise Education Case Studies and includes an example from Liverpool John Moores University School of Humanities and Social Science.
In addition this HEA case study describes the module Enterprise and Employability, a taught Environmental Sciences module at the University of Ulster.
Enterprise Educators UK (EEUK) regularly share members practice, including examples such as this 20-credit multi-level, multidisciplinary module "Making Ideas Happen" which introduces the fields of enterprise, entrepreneurship and innovation, whilst emphasising the generation and development of ideas with a distinctly social flavour.
BOSS stands for the Business Online Support Service, provided by Business Wales. This service provides online learning courses to help people who are thinking about, or actually, starting a business, already running a business or looking to grow their business.
Big Ideas Wales The Big Ideas Wales campaign is part of the Business Wales service, designed to support the next generation of young entrepreneurs in Wales.
Nesta Creative Enterprise Toolkit
Our enterprise resource toolkit contains tried and tested methods for teaching enterprise skills to creative individuals who are thinking about setting up a business. Available for purchase - with access to resources here http://www.nesta.org.uk/sites/default/files/cet_worksheets_case_studies_and_tutor_notes.pdf